




|
NanoSolutions Testing Facilities |
|
Streamlined Testing, Expert Results |
|
To contact us: |
|
Phone: 714-394-3628 E-mail: Bill@NanoSolutionsUSA.com |
|
ASTM F 1624 |
|
Significance This test method is used for research, design, service evaluation, manufacturing control, and development by quantitatively measuring stress parameters that are used in a design or failure analysis that takes into account the effects of environmental exposure including that which occurs during processing, such as plating.
Use ASTM F 1624 establishes a procedure to measure the susceptibility of steel to a time-delayed failure such as that caused by hydrogen. It does so by measuring the threshold for the onset of subcritical crack growth using standard fracture mechanics specimens, irregular-shaped specimens such as notched round bars, or actual product such as fasteners (threaded or unthreaded) springs or components.
The test is performed either in air, to measure the effect of residual hydrogen in the steel from processing (IHE), or in a controlled environment to measure the effect of hydrogen introduced into the steel as a result of the external sources of hydrogen (EHE).
|
|
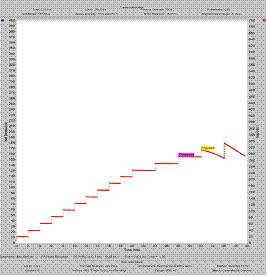
(10/5/2,4) RSL curve for 1”D bolt at 39 HRC with Pmax (cracked) and Pthreshold identified. |
Rising Step Load Method for Measuring Hydrogen Embrittlement |
|
Home > ASTM Standards > ASTM F 1624 |
|
For a Quote or if you have any Questions, give us a call or send us an e-mail
Phone: 714-394-3628 E-mail: Bill@NanoSolutionsUSA.com |

|
Irregular-shaped specimens fabricated from actual product can be tested as well. |